Basal Cell Carcinoma
What is Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)?
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer. BCC’s are abnormal, uncontrolled growths that arise from the skin’s basal cells in the outermost layer of skin (epidermis)
What causes BCC?
Most basal cell carcinomas are thought to be caused by the combination of intermittent, intense exposure, and cumulative to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight.
Where to look for BCC?
on skin THAT IS typically exposed to the sun, especially the face, ears, neck, scalp, shoulders and back. less frequently, they can be on any area of the skin.
How serious is BCC?
basal cell carcinomas can be disfiguring and uncomfortable - they can often be locally destructive if not detected and treated early. Occasionally these cancers metastasize (spread); and in very rare instances they can be fatal.
For most people, basal cell carcinoma is not life-threatening.
When to see a doctor?
if you observe changes in the appearance of your skin, such as a new growth, a change in a previous growth or a recurring sore.
People with the highest risk factors?
UV exposure from the sun or indoor tanning
History of Sunburns
Fair skin - Freckly, red or blond hair, and light-colored eyes
Age over 50 - however becoming more common for people in their 20’s & 30’s
Male gender
A personal or family history of skin cancer & Inherited syndromes that cause skin cancer
Radiation therapy
Immune-suppressing drugs
Exposure to arsenic
Chronic infections and skin inflammation from burns, scars and other conditions
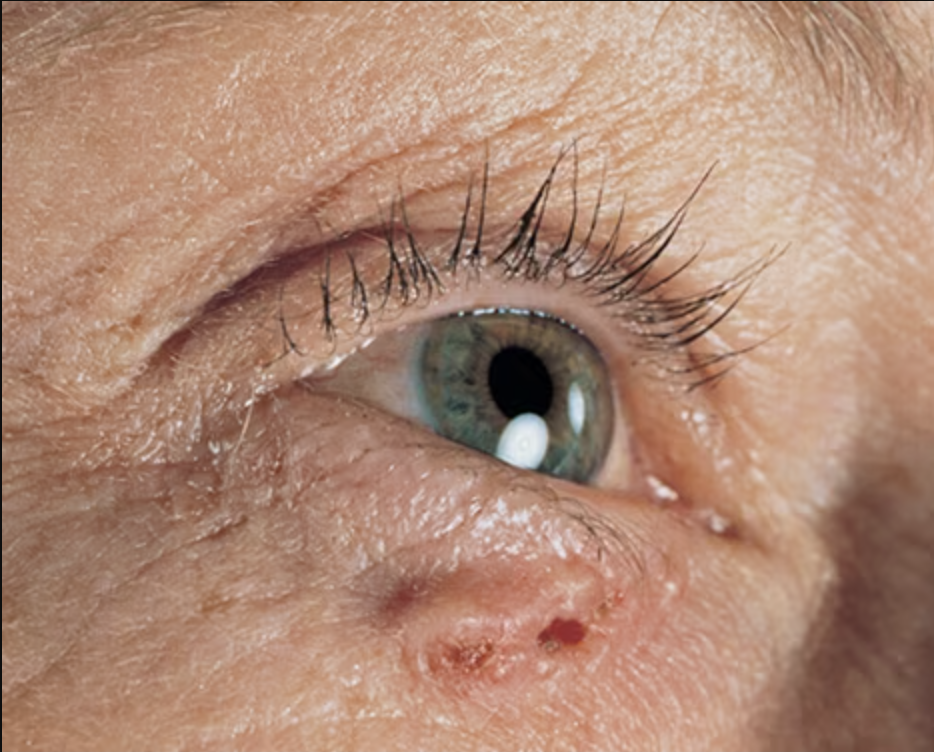

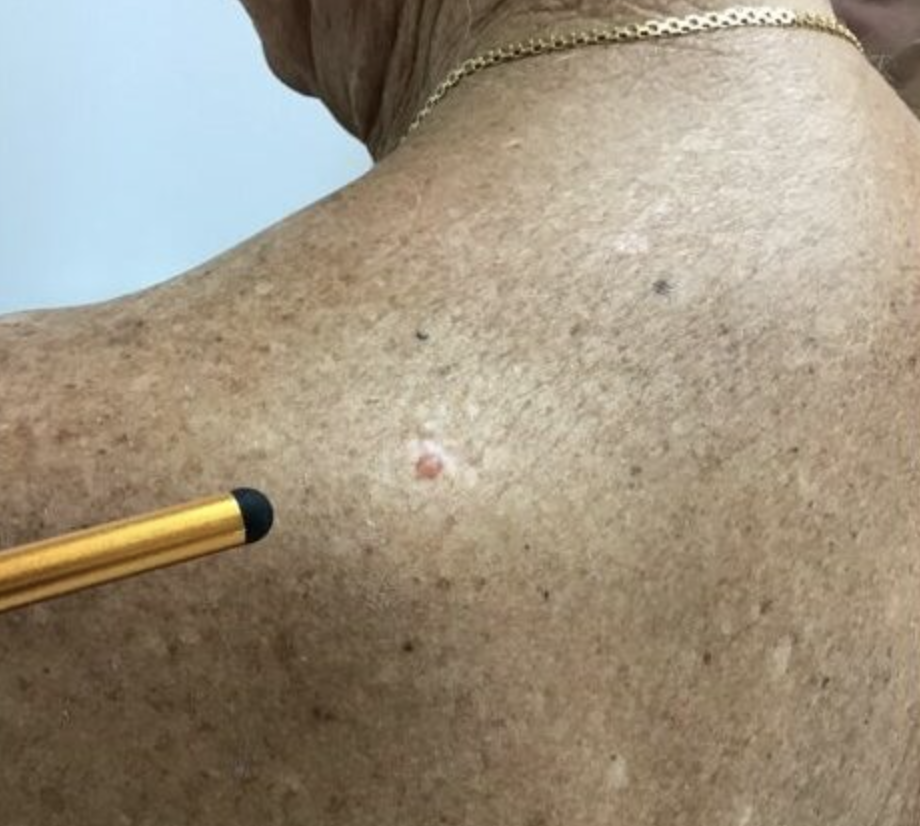
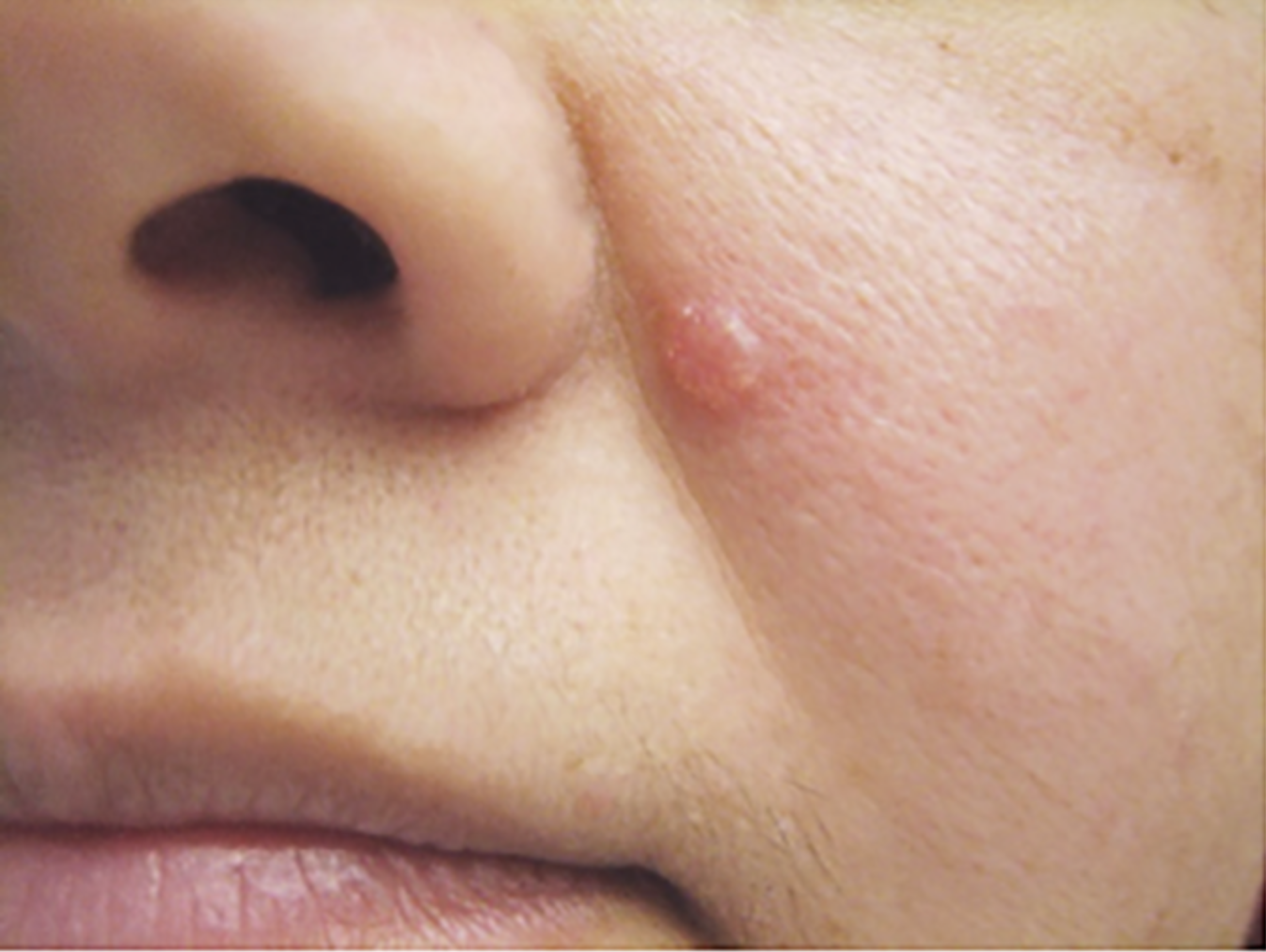
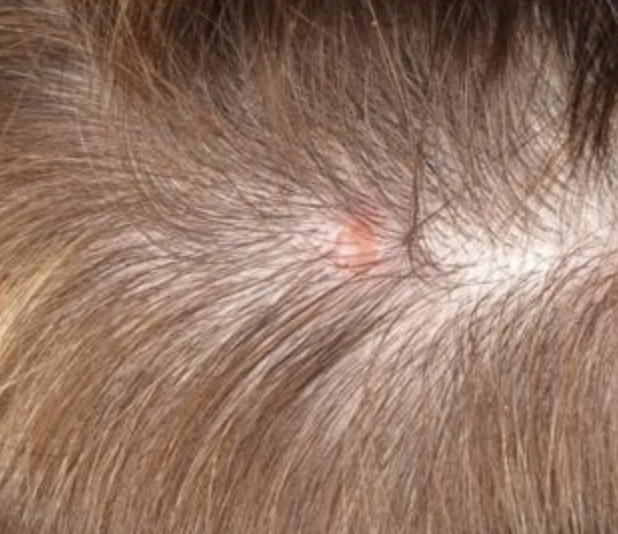
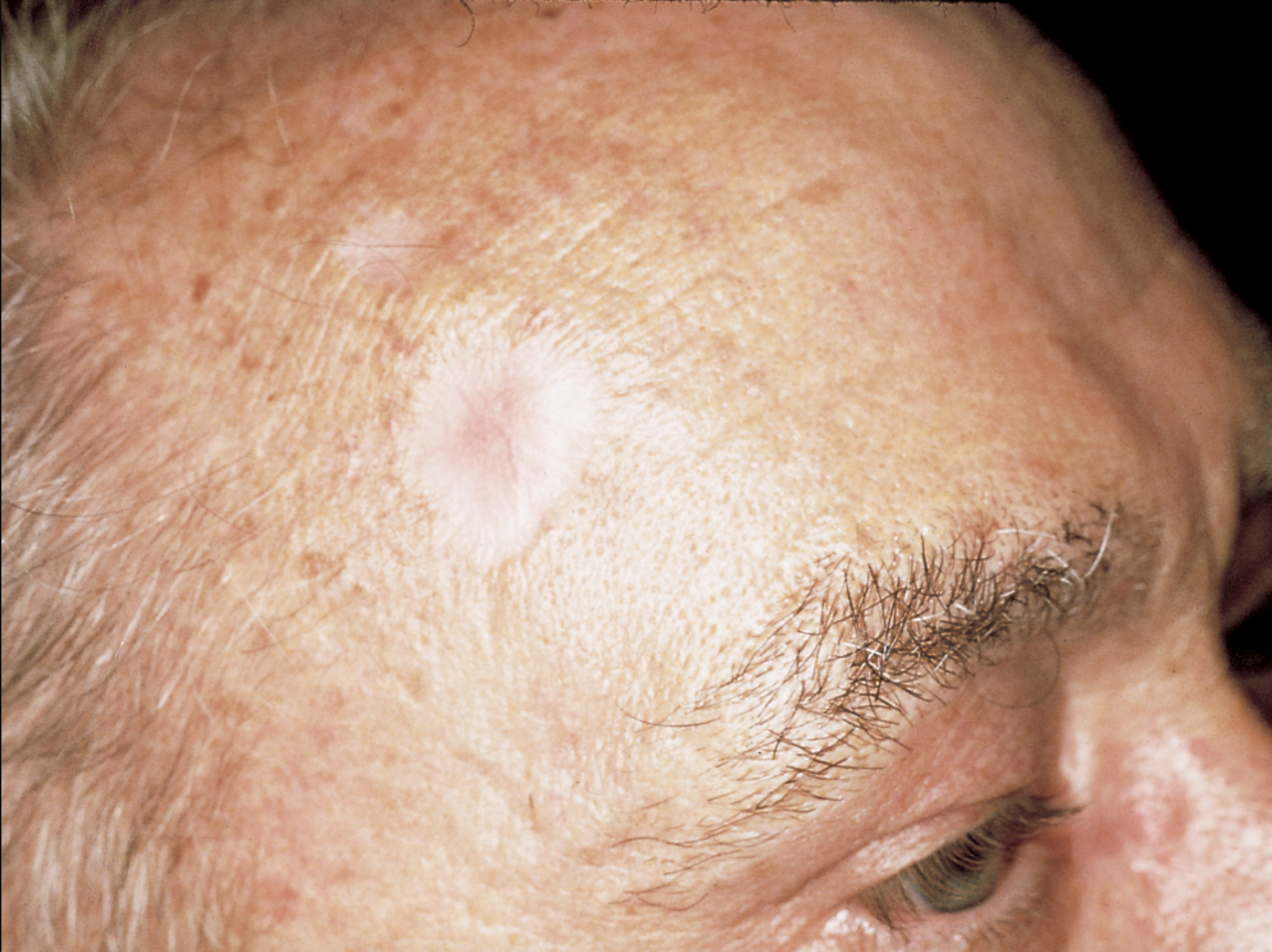
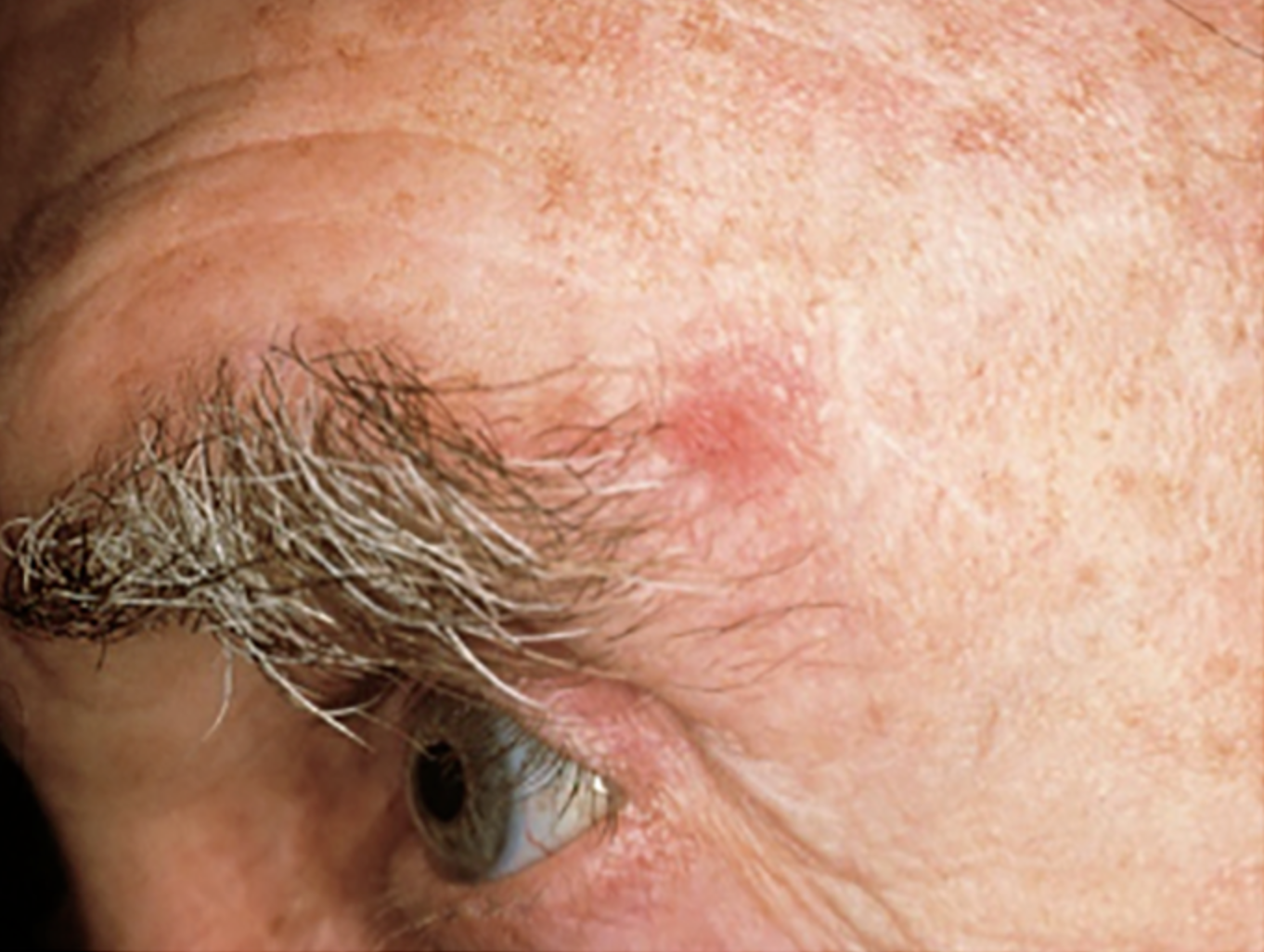
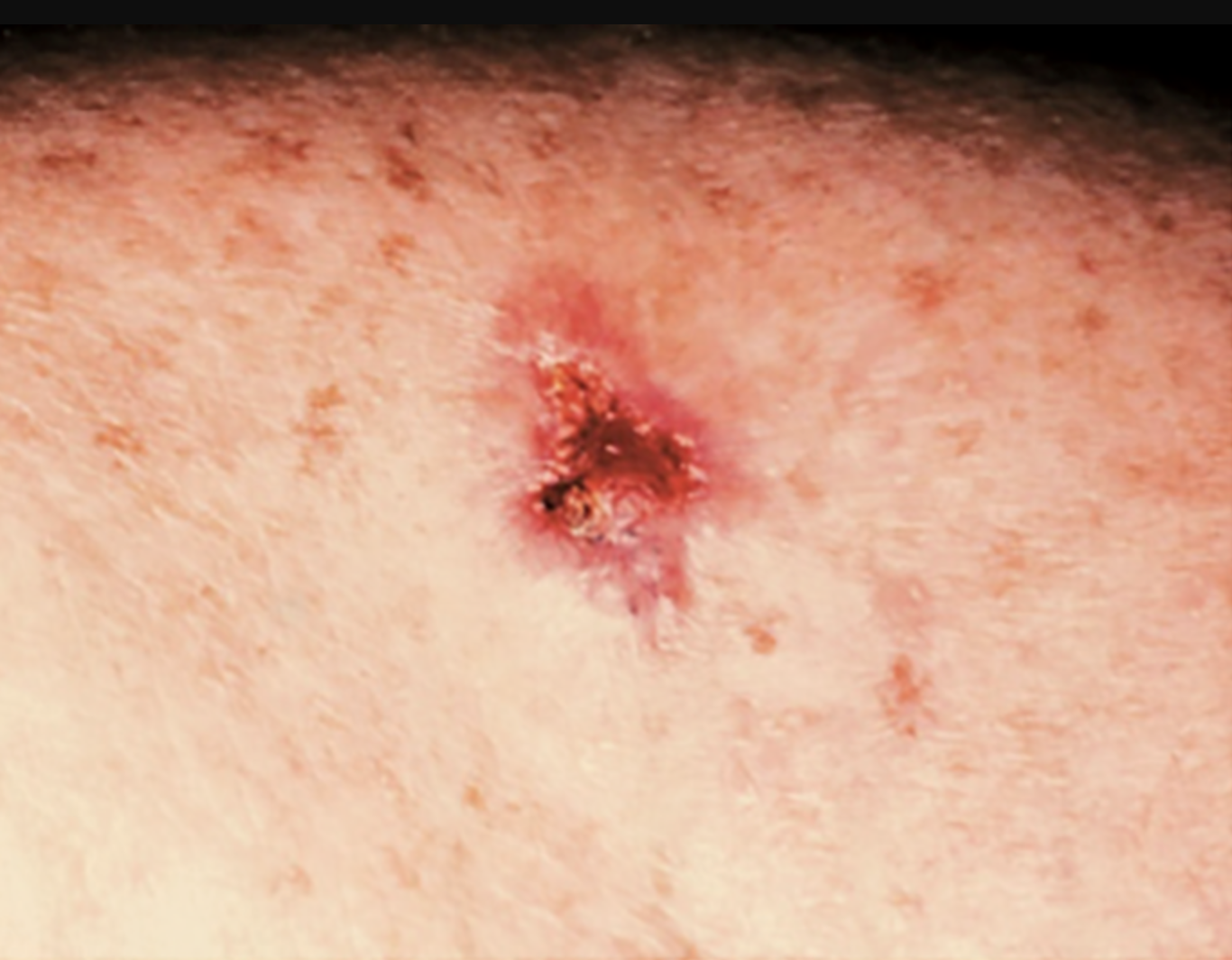
What to look for?
a change in the skin, such as a growth or a sore that won't heal. These changes in the skin (lesions) usually have one of the following characteristics:
A shiny, skin-colored bump that's translucent, meaning you can see a bit through the surface. The bump can look pearly white or pink on white skin. On brown and Black skin, the bump often looks brown or glossy black. Tiny blood vessels might be visible, though they may be difficult to see on brown and Black skin. The bump may bleed and scab over.
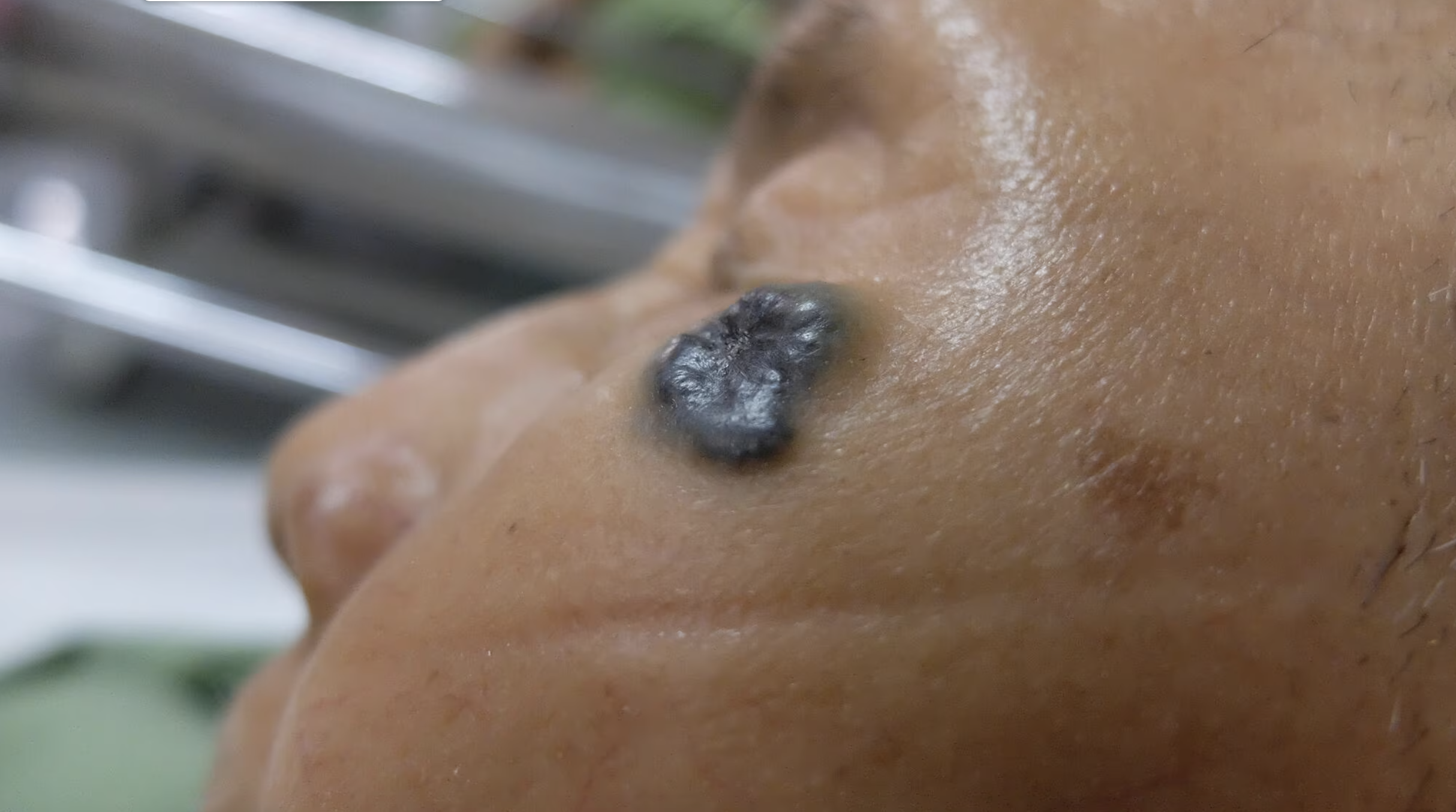
A brown, black or blue lesion — or a lesion with dark spots — with a slightly raised, translucent border.
A flat, scaly patch with a raised edge. Over time, these patches can grow quite large.
A white, waxy, scar-like lesion without a clearly defined border.
On brown and Black skin, basal cell carcinoma often looks like a bump that's brown or glossy black and has a rolled border.

